Elon Musk, SpaceX and Settlement of Human On Sister Planet Mars
Elon Musk, SpaceX and Settlement of Human On Sister Planet Mars
To achieve this goal, SpaceX is currently developing the Starship spacecraft, which is designed to transport humans and cargo to and from the surface of Mars. The company has conducted several successful test flights of prototypes of the spacecraft, and it is working towards sending humans to Mars as early as 2026.
Musk has stated that the first human mission to Mars will likely involve a small team of astronauts who will establish a base and begin preparing for future settlements. The long-term goal is to establish a permanent, self-sustaining human presence on the planet through the use of in situ resource utilization (ISRU) to produce food, water, and other resources necessary for human survival.
Overall, Musk's plan for settling humans on Mars involves a combination of technological development and long-term planning to establish a human presence on the planet that is capable of supporting itself over the long term.
What will SpaceX do after landing on planet Mars?
After landing on Mars, SpaceX's plans involve establishing a permanent, self-sustaining human settlement on the planet. This would likely involve building habitats and other infrastructure to support human life, as well as developing systems for producing food, water, and other necessary resources using in situ resource utilization (ISRU). SpaceX also plans to use Mars as a base for further exploration of the solar system, with the ultimate goal of establishing a permanent human presence on other planets and celestial bodies. In addition to these goals, SpaceX plans to use Mars as a testbed for developing technologies that could be used to help solve some of the biggest challenges facing humanity, such as climate change and the need for clean, renewable energy sources. Overall, SpaceX's plans for Mars involve establishing a permanent human presence on the planet and using it as a base for further exploration and the development of technologies that can benefit humanity.
Is life possible on Planet Mars? Is there underground Water?
There is evidence to suggest that Mars may have had conditions suitable for life in the past, and it is possible that microbial life could still exist on the planet today. In 2020, NASA's Perseverance rover discovered evidence of ancient microbial life on Mars in the form of fossilized microbial structures in rocks on the planet's surface. This discovery supports the idea that Mars may have had the necessary conditions for life to evolve at some point in its history. There is also evidence that liquid water may exist on Mars today, either in the form of underground lakes or as intermittent flows on the surface. In 2018, scientists detected what appeared to be a large, underground lake of liquid water beneath the planet's south polar ice cap, and there have been several other observations of possible water flows on the surface of the planet. Overall, while it is not yet certain whether life exists on Mars today, the evidence suggests that the planet may have had the necessary conditions for life in the past and may still have the potential to support life today.
How can we use Planet mar's atmosphere to create water and oxygen?
One way to use the atmosphere of Mars to create water and oxygen is through the process of in situ resource utilization (ISRU). This involves using the resources available on Mars to produce the materials necessary for human survival and exploration. One way to do this would be to use the planet's atmosphere, which is primarily composed of carbon dioxide (CO2), to produce oxygen and water. This could be done through a process called electrolysis, in which electricity is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The oxygen could then be used for breathing, while the hydrogen could be used as a fuel source. Another way to produce water and oxygen on Mars using the planet's atmosphere would be through the use of specialized equipment, such as a Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) system. This system would use a process called reverse electrolysis to break down CO2 molecules and produce oxygen and carbon monoxide (CO). The CO could then be converted back into CO2 and used in the process again, creating a closed-loop system for producing oxygen. Overall, there are several ways that the atmosphere of Mars could be used to create water and oxygen, which would be essential for supporting human life on the planet.
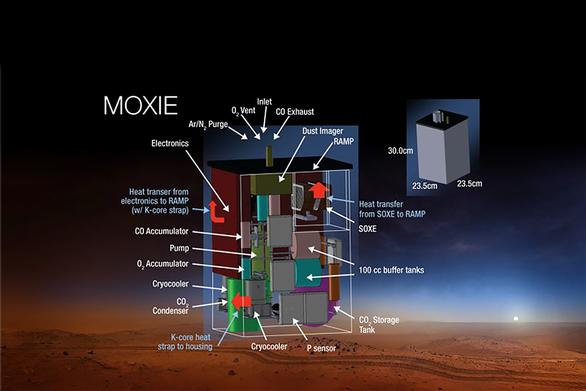
What is (MOXIE) system ? How does it works ?
The Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) is a system designed to produce oxygen from the carbon dioxide (CO2) present in the atmosphere of Mars. It was developed by NASA and is currently being tested on the Perseverance rover, which is currently exploring Mars. MOXIE works by using a process called reverse electrolysis to split CO2 molecules into oxygen and carbon monoxide (CO). The CO can then be converted back into CO2 and used in the process again, creating a closed-loop system for producing oxygen. The system consists of a small, box-like unit that is mounted on the rover. It contains a series of electrodes and filters that are used to separate the oxygen from the CO2. When the system is activated, it takes in a stream of Martian air and uses electricity to break down the CO2 molecules into their constituent parts. The oxygen is then collected and stored, while the CO is released back into the atmosphere. Overall, MOXIE is a promising technology that could potentially be used to produce oxygen on Mars, which would be essential for supporting human life on the planet.





Comments
Post a Comment